14 2.8 Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics
An earthquake is the shaking caused by the rupture (breaking) and subsequent displacement of rocks (one body of rock moving with respect to another) beneath Earth’s surface.
A body of rock that is under stress becomes deformed. When the rock can no longer withstand the deformation, it breaks and the two sides slide past each other. Because most rock is strong (unlike loose sand, for example), it can withstand a significant amount of deformation without breaking. But every rock has a deformation limit and will rupture (break) once that limit is reached. At that point, in the case of rocks within the crust, the rock breaks and there is displacement along the rupture surface. The magnitude of the earthquake depends on the extent of the area that breaks (the area of the rupture surface) and the average amount of displacement (sliding).
Most earthquakes take place near plate boundaries, but not necessarily right on a boundary, and not necessarily even on a pre-existing fault. The distribution of earthquakes across the globe is shown in Figure 2.8.1. It is relatively easy to see the relationships between earthquakes and the plate boundaries. Along divergent boundaries like the mid-Atlantic ridge and the East Pacific Rise, earthquakes are common, but restricted to a narrow zone close to the ridge, and consistently at less than 30 km depth. Shallow earthquakes are also common along transform faults, such as the San Andreas Fault. Along subduction zones earthquakes are very abundant, and they are increasingly deep on the landward side of the subduction zone.
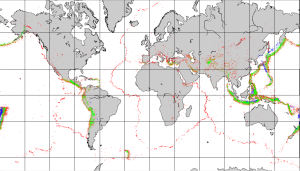
Earthquakes are also relatively common at a few intraplate locations. Some are related to the buildup of stress due to continental rifting or the transfer of stress from other regions, and some are not well understood. Examples of intraplate earthquake regions include the Great Rift Valley area of Africa, the Tibet region of China, and the Lake Baikal area of Russia.
Earthquakes at Divergent and Transform Boundaries
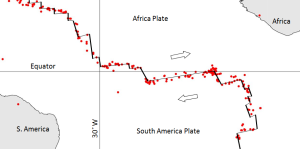
Figure 2.8.2 provides a closer look at magnitude (M) 4 and larger earthquakes in an area of divergent boundaries in the mid-Atlantic region near the equator. Here, as we saw in section 3.5, the segments of the mid-Atlantic ridge are offset by some long transform faults. Most of the earthquakes are located along the transform faults, rather than along the spreading segments, although there are clusters of earthquakes at some of the ridge-transform boundaries. Some earthquakes do occur on spreading ridges, but they tend to be small and infrequent because of the relatively high rock temperatures in the areas where spreading is taking place. Earthquakes along divergent and transform boundaries tend to be shallow, as the crust is not very thick.
Earthquakes at Convergent Boundaries
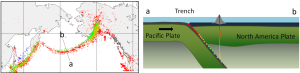
The distribution and depths of earthquakes in the North Pacific are shown in Figure 2.8.3. In this region, the Pacific Plate is subducting beneath the North America Plate, creating the Aleutian Trench and the Aleutian Islands. Shallow earthquakes are common along the trench, but there is also significant earthquake activity extending down several hundred kilometers, as the subducting plate continues to interact at depth with the overriding plate. The earthquakes get deeper with distance from the trench; note in the left panel in Figure 2.8.3 that as you move along the transect from point a to point b, there is a trend of increasing earthquake depth. This reveals that it is the Pacific Plate that is moving northwards and being subducted.
The distribution of earthquakes in the area of the India-Eurasia plate boundary is shown in Figure 2.8.4. This is a continent-continent convergent boundary, and it is generally assumed that although the India Plate continues to move north toward the Asia Plate, there is no actual subduction taking place. There are transform faults on either side of the India Plate in this area.
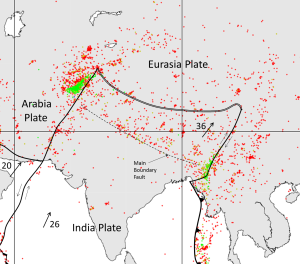
The entire northern India and southern Asia region is very seismically active. Earthquakes are common in northern India, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh and adjacent parts of China, and throughout Pakistan and Afghanistan. Many of the earthquakes are related to the transform faults on either side of the India Plate, and most of the others are related to the significant tectonic squeezing caused by the continued convergence of the India and Asia Plates. That squeezing has caused the Asia Plate to be thrust over top of the India Plate, building the Himalayas and the Tibet Plateau to enormous heights.
Written by Dr. Cristina Cardona.
Marine Reptiles
Marine reptiles are cold blooded (ectothermic), meaning that their internal temperature is regulated by their surroundings and is not constant. They have scales that cover their bodies, they reproduce out of the water, and they evolved from amphibians. Today's marine reptiles include turtles, sea snakes, iguanas, and marine crocodiles.
Sea Turtles:
- 5 widely distributed tropical and subtropical species:
- Green, Hawksbill, Ridley, Leatherback and Loggerback
- All have large limbs and non-retractable heads
- All are excellent swimmers: the front limbs are flattened to act as oars, while the hind limbs work as rudders
- All grow to considerable size: the Atlantic Leatherback is the largest, growing to more than 1500 lbs and 11.5 ft long
- All are under threat of extinction
- The Green turtle is known for its long migrations, often of more than a thousand miles, between its feeding grounds and breeding areas
- Some use smell and vision, wave patterns, the angle of the sun and even celestial navigation to find a beach site close to where they were hatched
- if they survived there, then their offspring is more likely to survive
- https://www.seeturtles.org/sea-turtle-facts
Sea snakes:
- There are more than 50 species, which represent the most recently evolved group of marine reptiles
- They're found primarily in the warm oceans of the Indo-Pacific, but some can be found in the Atlantic (as seen in my photo)
- They grow to lengths of 4 to 10 feet
- Their bodies are flattened for swimming
- They breathe air, but have valves on their noses and can dive for crustaceans or shellfish
- They're truly marine except for one species that lays eggs on land – most give live birth at sea
- They also feed on small fish
- by catching and holding them in their jaws with their small teeth until their venom seeps into the wounds and kills the prey
- Their venom is among the most active of all known biological poisons
- the physiological effects are similar to those of cobra venom, only several times more toxic
- Fortunately for humans, they lack fangs to inject the venom and they are not terribly aggressive
- However, several people a year die from the bites of sea snakes, mostly fishermen who accidentally get bitten while removing them from their nets

Marine Iguanas:
- Found in the Galapagos Islands
- They're large, heavy and sluggish on land, but much more graceful in the sea
- They eat encrusting algae that they scrape from rocks with their spade-like teeth
Marine Crocodiles:
- These are occasional seafarers
- And are found mostly in the Indo-Pacific area from India to Australia
- They may grow to 30 ft in length
- They may be endangered because of predation by humans
Dr. Cristina Cardona

