9.6 Preventing Infection
Open Resources for Nursing (Open RN)
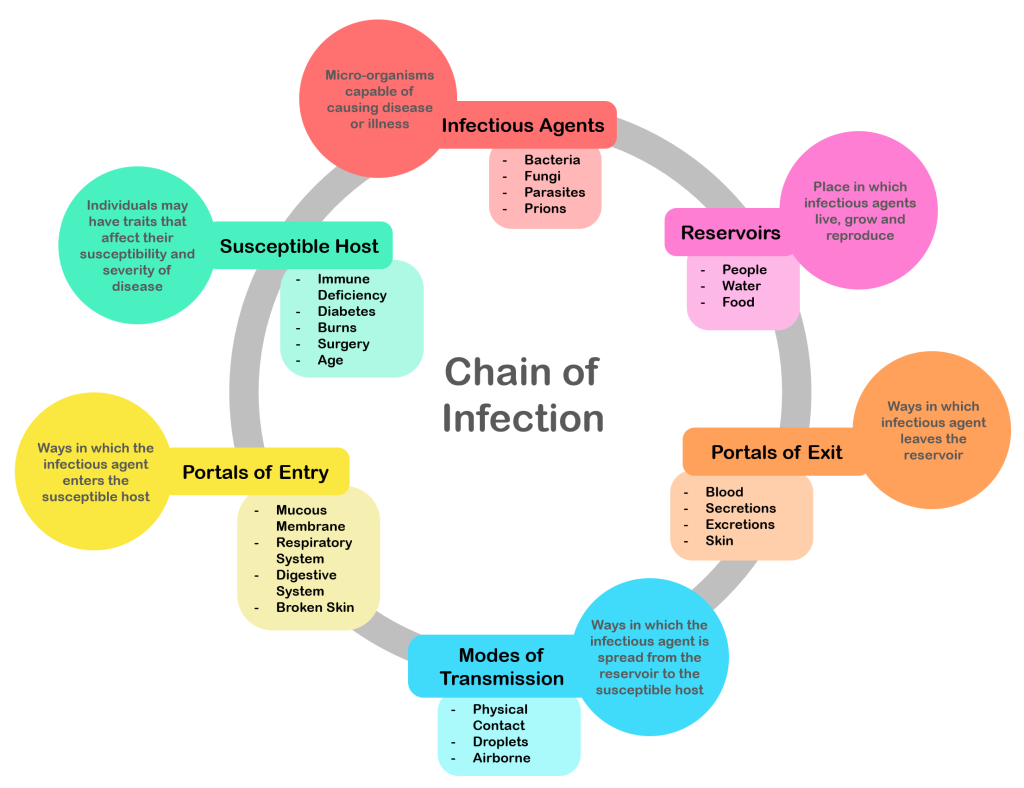
In addition to recognizing signs of infection and educating clients about the treatment of their infection, nurses also play an important role in preventing the spread of infection. A cyclic process known as the chain of infection describes the transmission of an infection. By implementing interventions to break one or more links in the chain of infection, the spread of infection can be stopped. See Figure 9.16[1] for an illustration of the links within the chain of infection. These links are described as the following[2]:
- Infectious Agent: A causative organism, such as bacteria, virus, fungi, parasite.
- Reservoir: A place where the organism grows, such as in blood, food, or a wound.
- Portal of Exit: The method by which the organism leaves the reservoir, such as through respiratory secretions, blood, urine, breast milk, or feces.
- Mode of Transmission: The vehicle by which the organism is transferred such as physical contact, inhalation, or injection. The most common vehicles are respiratory secretions spread by a cough, sneeze, or on the hands. A single sneeze can send thousands of virus particles into the air.
- Portal of Entry: The method by which the organism enters a new host, such as through mucous membranes or nonintact skin.
- Susceptible Host: The susceptible individual the organism has invaded.
For a pathogen to continue to exist, it must put itself in a position to be transmitted to a new host, leaving the infected host through a portal of exit. Similar to portals of entry, the most common portals of exit include the skin and the respiratory, urogenital, and gastrointestinal tracts. Coughing and sneezing can expel thousands of pathogens from the respiratory tract into the environment. Other pathogens are expelled through feces, urine, semen, and vaginal secretions. Pathogens that rely on insects for transmission exit the body in the blood extracted by a biting insect.[3]
The pathogen enters a new individual via a portal of entry, such as mucous membranes or nonintact skin. If the individual has a weakened immune system or their natural defenses cannot fend off the pathogen, they become infected.
Interventions to Break the Chain of Infection
Infections can be stopped from spreading by interrupting this chain at any link. Chain links can be broken by disinfecting the environment, sterilizing medical instruments and equipment, covering coughs and sneezes, using good hand hygiene, implementing standard and transmission-based precautions, appropriately using personal protective equipment, encouraging clients to stay up-to-date on vaccines (including the flu shot), following safe injection practices, and promoting the optimal functioning of the natural immune system with good nutrition, rest, exercise, and stress management.
Disinfection and Sterilization
Disinfection and sterilization are used to kill microorganisms and remove harmful pathogens from the environment and equipment to decrease the chance of spreading infection. Disinfection is the removal of microorganisms. However, disinfection does not destroy all spores and viruses. Sterilization is a process used on equipment and the environment to destroy all pathogens, including spores and viruses. Sterilization methods include steam, boiling water, dry heat, radiation, and chemicals. Because of the harshness of these sterilization methods, skin can only be disinfected and not sterilized.[4]
Standard and Transmission-Based Precautions
To protect clients and health care workers from the spread of pathogens, the CDC has developed precautions to use during client care that address portals of exit, methods of transmission, and portals of entry. These precautions include standard precautions and transmission-based precautions.
Standard Precautions
Standard precautions are used when caring for all clients to prevent healthcare-associated infections. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), standard precautions are the minimum infection prevention practices that apply to all client care, regardless of suspected or confirmed infection status of the client, in any setting where health care is delivered. These precautions are based on the principle that all blood, body fluids (except sweat), nonintact skin, and mucous membranes may contain transmissible infectious agents. These standards reduce the risk of exposure for the health care worker and protect the client from potential transmission of infectious organisms.[5] See Figure 9.17[6] for an image of some of the components of standard precautions.
Current standard precautions according to the CDC include the following:
- Appropriate hand hygiene
- Use of personal protective equipment (e.g., gloves, gowns, masks, eyewear) whenever infectious material exposure may occur
- Appropriate client placement and care using transmission-based precautions when indicated
- Respiratory hygiene/cough etiquette
- Proper handling and cleaning of environment, equipment, and devices
- Safe handling of laundry
- Sharps safety (i.e., engineering and work practice controls)
- Aseptic technique for invasive nursing procedures such as parenteral medication administration[7]
![]“hand-disinfection-4954840_960_720.jpg” by KlausHausmann is licensed under CC0 Image showing hand sanitizer, gloves, and a surgical mask](https://opencontent.ccbcmd.edu/app/uploads/sites/32/2024/08/hand-sanitizer-300x201.png)
Hand Hygiene
Hand hygiene, although simple, is still the best and most effective way to prevent the spread of infection. The 2021 National Patient Safety Goals from The Joint Commission encourages infection prevention strategy practices such as implementing the hand hygiene guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control.[8] Accepted methods for hand hygiene include using either soap and water or alcohol-based hand sanitizer. It is essential for all health care workers to use proper hand hygiene at the appropriate times, such as the following:
- Immediately before touching a client
- Before performing an aseptic task or handling invasive devices
- Before moving from a soiled body site to a clean body site on a client
- After touching a client or their immediate environment
- After contact with blood, body fluids, or contaminated surfaces (with or without glove use)
- Immediately after glove removal[9]
Hand hygiene also includes health care workers keeping their nails short with tips less than 0.5 inches and no nail polish. Nails should be natural, and artificial nails or tips should not be worn. Artificial nails and chipped nail polish have been associated with a higher level of pathogens carried on the hands of the nurse despite hand hygiene.[10]
Respiratory Hygiene/Cough Etiquette
Respiratory hygiene is targeted at clients, accompanying family members and friends, and staff members with undiagnosed transmissible respiratory infections. It applies to any person with signs of illness, including cough, congestion, or increased production of respiratory secretions when entering a health care facility. The elements of respiratory hygiene include the following:
- Education of health care facility staff, clients, and visitors
- Posted signs, in language(s) appropriate to the population served, with instructions to clients and accompanying family members or friends
- Source control measures for a coughing person (e.g., covering the mouth/nose with a tissue when coughing and prompt disposal of used tissues, or applying surgical masks on the coughing person to contain secretions)
- Hand hygiene after contact with one’s respiratory secretions
- Spatial separation, ideally greater than three feet, of persons with respiratory infections in common waiting areas when possible[11]
Health care personnel are advised to wear a mask and use frequent hand hygiene when examining and caring for clients with signs and symptoms of a respiratory infection. Health care personnel who have a respiratory infection are advised to stay home or avoid direct client contact, especially with high-risk clients. If this is not possible, then a mask should be worn while providing client care.[12]
Personal Protective Equipment
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) includes gloves, gowns, face shields, goggles, and masks used to prevent the spread of infection to and from clients and health care providers. See Figure 9.18[13] for an image of a nurse wearing PPE. Depending upon the anticipated exposure and type of pathogen, PPE may include the use of gloves, a fluid-resistant gown, goggles or a face shield, and a mask or respirator. When used while caring for a client with transmission-based precautions, PPE supplies are typically stored in an isolation cart next to the client’s room.

Transmission-Based Precautions
In addition to standard precautions, transmission-based precautions are used for clients with documented or suspected infection of highly transmissible pathogens, such as C. difficile (C-diff), Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE), Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), measles, and tuberculosis (TB). For clients with these types of pathogens, standard precautions are used along with specific transmission-based precautions.[14]
There are three categories of transmission-based precautions: contact precautions, droplet precautions, and airborne precautions. Transmission-based precautions are used when the route(s) of transmission of a specific disease are not completely interrupted using standard precautions alone.
Some diseases, such as tuberculosis, have multiple routes of transmission so more than one transmission-based precaution category must be implemented. See Table 9.6 outlining the categories of transmission precautions with associated PPE and other precautions. When possible, clients with transmission-based precautions should be placed in a single occupancy room with dedicated client care equipment (e.g., blood pressure cuffs, stethoscope, and thermometer stay in the client’s room). A card is posted outside the door alerting staff and visitors to required precautions before entering the room. See Figure 9.19[15] for an example of signage used for a client with contact precautions. Transport of the clientand unnecessary movement outside the client room should be limited. When transmission-based precautions are implemented, it is also important for the nurse to make efforts to counteract possible adverse effects of these precautions on clients, such as anxiety, depression, perceptions of stigma, and reduced contact with clinical staff.[16]
Table 9.6 Transmission-Based Precautions[17]
| Precaution | Implementation | PPE and Other Precautions |
|---|---|---|
| Contact | Known or suspected infections with increased risk for contact transmission (e.g., draining wounds, fecal incontinence) or with epidemiologically important organisms, such as C-diff, MRSA, VRE, or RSV | Gloves
Gown Dedicated equipment Limit client transport out of room Prioritized disinfection of the room Note: Use only soap and water for hand hygiene in clients with C. difficile infection. |
| Droplet | Known or suspected infection with pathogens transmitted by large respiratory droplets generated by coughing, sneezing, or talking, such as influenza or pertussis | Mask
Goggles or face shield Dedicated equipment |
| Airborne | Known or suspected infection with pathogens transmitted by small respiratory droplets that travel through the air, such as measles and coronavirus | Fit-tested N-95 respirator
Airborne infection isolation room Single-client room Client door closed Restricted susceptible personnel room entry Dedicated equipment |

Client Transport
Several principles are used to guide transport of clients requiring transmission-based precautions. During inpatient and residential settings, these principles include the following:
- Limit transport for essential purposes only, such as diagnostic and therapeutic procedures that cannot be performed in the client’s room
- When transporting, use appropriate barriers on the client consistent with the route and risk of transmission (e.g., mask, gown, covering the affected areas when infectious skin lesions or drainage is present)
- Notify health care personnel in the receiving area of the impending arrival of the client and of the precautions necessary to prevent transmission[18]
Enteric Precautions
Enteric precautions are used when there is the presence, or suspected presence, of gastrointestinal pathogens such as Clostridium difficile (C-diff) or norovirus. These pathogens are present in feces, so health care workers should always wear a gown in the client room to prevent inadvertent fecal contamination of their clothing from contact with contaminated surfaces.
In addition to contact precautions, enteric precautions include the following:
- Using only soap and water for hand hygiene. Do not use hand sanitizer because it is not effective against C-diff spores.
- Using a special disinfecting process. Special disinfecting should be used after client discharge and includes disinfection of the mattress.
Reverse Isolation
Reverse isolation, also called neutropenic precautions, is used for clients who have compromised immune systems and low neutrophil levels. This type of isolation protects the client from pathogens in their environment. In addition to using contact precautions to protect the client, reverse isolation precautions include the following:
- Meticulous hand hygiene by all visitors, staff, and the client
- Frequently monitoring for signs and symptoms of infection and sepsis
- Not allowing live plants, fresh flowers, fresh raw fruits or vegetables, sushi, deli foods, or cheese into the room due to bacteria and fungi
- Placement in a private room or a positive pressure room
- Limited transport and movement of the client outside of the room
- Masking of the client for transport with a surgical mask[19]
Psychological Effects of Isolation
Although the use of transmission-based precautions is needed to prevent the spread of infection, it is important for nurses to be aware of the potential psychological impact on the client. Research has shown that isolation can cause negative impact on client mental well-being and behavior, including higher scores for depression, anxiety, and anger among isolated clients. It has also been found that health care workers spend less time with clients in isolation, resulting in a negative impact on client safety.[20]
Client and family education at the time of instituting transmission-based precautions is a critical component of the process to reduce anxiety and distress. Clients often feel stigmatized when placed in isolation, so it is important for them to understand the rationale of the precautions to keep themselves and others free from the spread of disease. Preparing clients emotionally will also help decrease their anxiety and help them cope with isolation.[21] It is also important to provide distractions from boredom, such as music, television, video games, magazines, or books, as appropriate. Simple actions, such as charting while in the client’s room, can also increase nurse-client interaction time.
Aseptic and Sterile Techniques
In addition to using standard precautions and transmission-based precautions, aseptic technique (also called medical asepsis) is used to prevent the transfer of microorganisms from one person or object to another during a medical procedure. For example, a nurse administering parenteral medication or performing urinary catheterization uses aseptic technique. When performed properly, aseptic technique prevents contamination and transfer of pathogens to the client from caregiver hands, surfaces, and equipment during routine care or procedures. It is important to remember that potentially infectious microorganisms can be present in the environment, on instruments, in liquids, on skin surfaces, or within a wound.[22]
There is often misunderstanding between the terms aseptic technique and sterile technique in the health care setting. Both asepsis and sterility are closely related with the shared concept being the removal of harmful microorganisms that can cause infection. In the most simplistic terms, aseptic technique involves creating a protective barrier to prevent the spread of pathogens, whereas sterile technique is a purposeful attack on microorganisms. Sterile technique (also called surgical asepsis) seeks to eliminate every potential microorganism in and around a sterile field while also maintaining objects as free from microorganisms as possible. Sterile fields are implemented during surgery, as well as during nursing procedures such as the insertion of a urinary catheter, changing dressings on open wounds, and performing central line care. See Figure 9.20[23] for an image of a sterile field during surgery. Sterile technique requires a combination of meticulous handwashing, creating and maintaining a sterile field, using long-lasting antimicrobial cleansing agents such as Betadine, donning sterile gloves, and using sterile devices and instruments.[24]
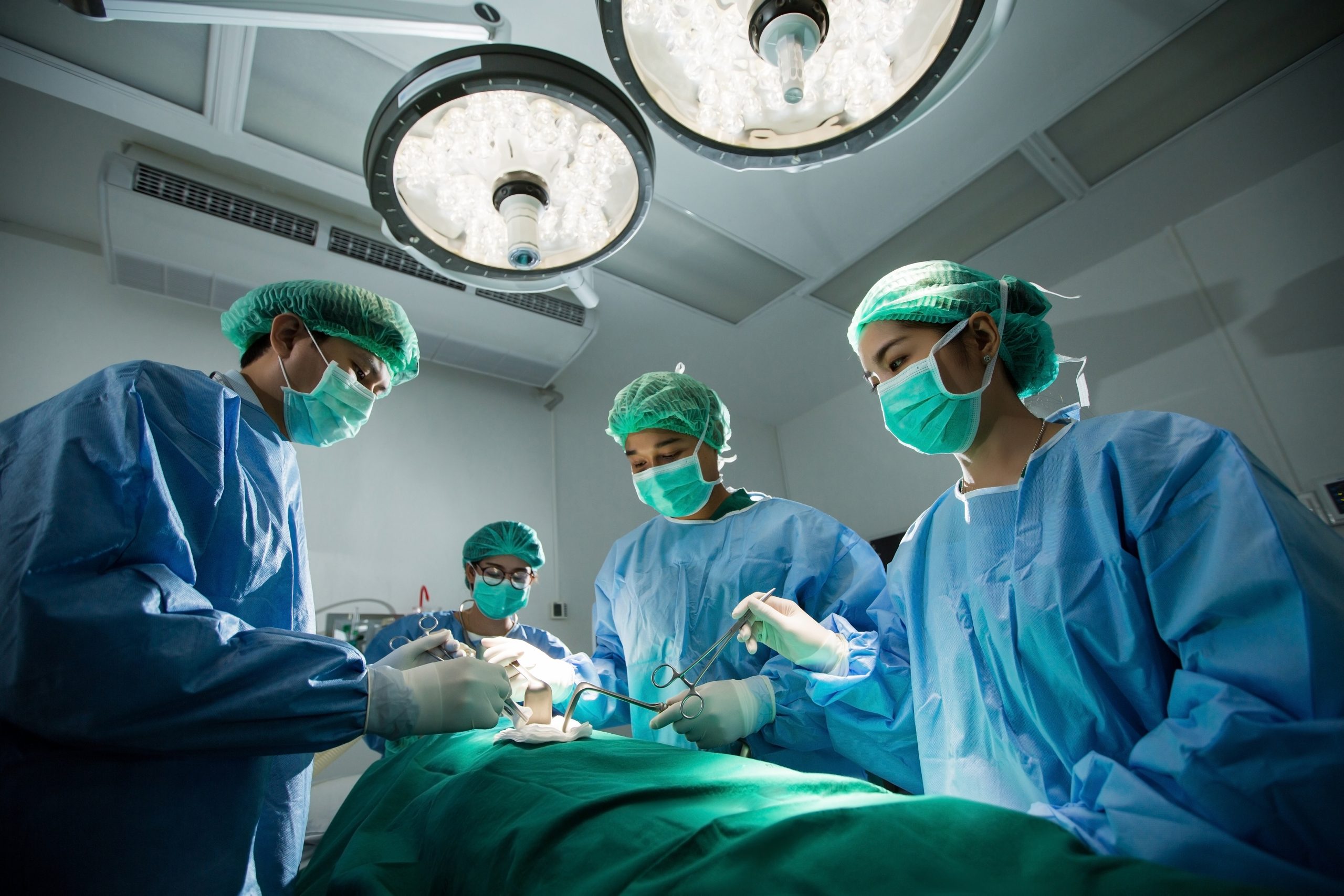
Read additional information about aseptic and sterile technique in the “Aseptic Technique” in Open RN Nursing Skills, 2e.
Read a continuing education article about Sterile Technique and surgical scrubbing.
Other Hygienic Client Care Interventions
In addition to implementing standard and transmission-based precautions and utilizing aseptic and sterile technique when performing procedures, nurses implement many interventions to place a client in the best health possible to prevent an infection or treat infection. These interventions include actions like encouraging rest and good nutrition, teaching stress management, providing good oral care, encouraging daily bathing, and changing linens. It is also important to consider how gripper socks, mobile devices, and improper glove usage can contribute to the transmission of pathogens.
Oral Care
Client hygiene is important in the prevention and spread of infection. Although oral care may be given a low priority, research has found that poor oral care is associated with the spread of infection, poor health outcomes, and poor nutrition. Oral care should be performed in the morning, after meals, and before bed.[25]
Daily Bathing
Daily bathing is another intervention that may be viewed as time-consuming and receive low priority, but it can have a powerful impact on decreasing the spread of infection. Studies have shown a significant decrease in healthcare-associated infections with daily bathing using chlorhexidine gluconate (CHG) wipes or solution. The use of traditional soap and water baths do not reduce infection rates as significantly as CHG products, and wash basins have also been shown to be a reservoir for pathogens.[26]
Linens
Changing bed linens, towels, and a gown regularly eliminates potential reservoirs of bacteria. Fresh linens also promote client comfort.
Gripper Socks
Have you ever thought about what happens to the bed linens when a client returns from a walk in the hallway with gripper socks and gets back into bed with these socks? Research demonstrates that pathogens from the floor are transferred to the client’s bed linens from the gripper socks. Nurses should remove gripper socks that were used for walking before clients climb into bed. They should also throw the socks away when the client is discharged instead of sending them home.[27]
Cellular Phones and Mobile Devices
Research has shown that cell phones and mobile devices carry many pathogens and are dirtier than a toilet seat or the bottom of a shoe. Clients, staff, and visitors routinely bring these mobile devices into health care facilities, which can cause the spread of disease. Nurses should frequently wipe mobile devices with disinfectant. They should encourage clients and visitors to disinfect phones frequently and avoid touching the face after having touched a mobile device.[28]
Gloves
Although gloves are used to prevent the spread of infection, they can also contribute to the spread of infection if used improperly. For example, research has shown that hand hygiene opportunities are being missed because of the overuse of gloves. For example, a nurse may don gloves to suction a client but neglect to remove them and perform hand hygiene before performing the next procedure on the same client. This can potentially cause the spread of secondary infection. The World Health Organization (WHO) states that gloves should be worn when there is an expected risk of exposure to blood or body fluids or to protect the hands from chemicals and hazardous drugs, but hand hygiene is the best method of disease prevention and is preferred over wearing gloves when the exposure risk is minimal. Nurses have the perception that wearing gloves provides extra protection and cleanliness. However, the opposite is true. Nonsterile gloves have a high incidence of contamination with a range of bacteria, which means that a gloved hand is dirtier than a washed hand. Research has shown that nearly 40% of the times that gloves are used in client care, there is cross contamination. The most striking example of cross contamination includes situations when gloves are used for toileting a client and not being removed before touching other surfaces or the client.[29],[30],[31]
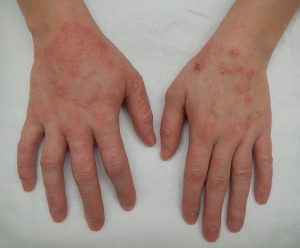
Glove-related contact dermatitis has also become an important issue in recent years as more and more nurses are experiencing damage to the hands. Contact dermatitis can develop from repeated use of gloves and develops as dry, itchy, irritated areas on the skin of the hands. See Figure 9.21[32] for an image of contact dermatitis from gloves. Because the skin is the first line of defense in preventing pathogens from entering the body, maintaining intact skin is very important to prevent nurses from exposure to pathogens.
- “Chain_of_Infection.png” by Genieieiop is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0 ↵
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). Chain of infection components. https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/learning/safetyculturehc/module-2/3.html ↵
- This work is a derivative of Microbiology by OpenStax and is licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2019, May 24). Disinfection and sterilization. https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/disinfection/index.html ↵
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2016, January 26). Standard precautions for all patient care. https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/basics/standard-precautions.html ↵
- “hand-disinfection-4954840_960_720.jpg” by KlausHausmann is licensed under CC0 ↵
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2016, January 26). Standard precautions for all patient care. https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/basics/standard-precautions.html ↵
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2019, April 29). Hand hygiene in healthcare settings. https://www.cdc.gov/handhygiene/ ↵
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2019, April 29). Hand hygiene in healthcare settings. https://www.cdc.gov/handhygiene/ ↵
- Blackburn, L., Acree, K., Bartley, J., DiGiannantoni, E., Renner, E., & Sinnott, L. T. (2020). Microbial growth on the nails of direct patient care nurses wearing nail polish. Nursing Oncology Forum, 47(2), 155-164. https://doi.org/10.1188/20.onf.155-164 ↵
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2016, January 26). Standard precautions for all patient care. https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/basics/standard-precautions.html ↵
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2016, January 26). Standard precautions for all patient care. https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/basics/standard-precautions.html ↵
- “U.S. Navy Doctors, Nurses and Corpsmen Treat COVID Patients in the ICU Aboard USNS Comfort (49825651378).jpg” by Navy Medicine is licensed under CC0. ↵
- Siegel, J. D., Rhinehart, E., Jackson, M., Chiarello, L., & Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. (2019, July 22). 2007 guideline for isolation precautions: Preventing transmission of infectious agents in healthcare settings. https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/isolation/index.html ↵
- “Contact_Precautions_poster.pdf” by U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is in the Public Domain ↵
- Siegel, J. D., Rhinehart, E., Jackson, M., Chiarello, L., & Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. (2019, July 22). 2007 guideline for isolation precautions: Preventing transmission of infectious agents in healthcare settings. https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/isolation/index.html ↵
- Siegel, J. D., Rhinehart, E., Jackson, M., Chiarello, L., & Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. (2019, July 22). 2007 guideline for isolation precautions: Preventing transmission of infectious agents in healthcare settings. https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/isolation/index.html ↵
- Siegel, J. D., Rhinehart, E., Jackson, M., Chiarello, L., & Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. (2019, July 22). 2007 guideline for isolation precautions: Preventing transmission of infectious agents in healthcare settings. https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/isolation/index.html ↵
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (n.d.). What you need to know: Neutropenia and risk for infection. https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/preventinfections/pdf/neutropenia.pdf ↵
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (2020, January 15). Health care-associated infections. https://health.gov/our-work/health-care-quality/health-care-associated-infections ↵
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (2020, January 15). Health care-associated infections. https://health.gov/our-work/health-care-quality/health-care-associated-infections ↵
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020, August 10). Glossary of terms for infection prevention and control in dental settings. https://www.cdc.gov/oralhealth/infectioncontrol/glossary.htm ↵
- “226589236-huge.jpg” by TORWAISTUDIO is used under license from Shutterstock.com ↵
- This work is a derivative of StatPearls by Tennant and Rivers and is licensed under CC BY 4.0. ↵
- Ackley, B., Ladwig, G., Makic, M. B., Martinez-Kratz, M., & Zanotti, M. (2020). Nursing diagnosis handbook: An evidence-based guide to planning care (12th ed.). Elsevier. pp. 546-552, 828-832. ↵
- Salamone, K., Yacoub, E., Mahoney, A. M., & Edward, K. L. (2013). Oral care of hospitalised older patients in the acute medical setting. Nursing Research and Practice, 2013, 827670. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/827670 ↵
- Welle, M. K., Bliha, M., DeLuca, J., Frauhiger, A., & Lamichhane-Khadka, R. (2019, January/February). Bacteria on the soles of patient-issued nonskid slipper socks: An overlooked pathogen spread threat? Orthopedic Nursing, 38(1), 33-40. https://doi.org/10.1097/nor.0000000000000516 ↵
- Morubagal, R. R., Shivappa, S. G., Mahale, R. P., & Neelambike, S. M. (2017). Study of bacterial flora associated with mobile phones of healthcare workers and non-healthcare workers. Iranian Journal of Microbiology, 9(3), 143–151. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5719508/ ↵
- Burdsall, D. P., Gardner, S. E., Cox, T., Schweizer, M., Culp, K. R., Steelman, V. M., & Herwaldt, L. A. (2017). Exploring inappropriate certified nursing assistant glove use in long-term care. American Journal of Infection Control, 45(9), 940-945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2017.02.017 ↵
- Jain, S., Clezy, K., & McLaws, M. L. (2017, October 15). Glove: Use for safety or overuse? American Journal of Infection Control, 45(12), 1407-1410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2017.08.029 ↵
- Welle, M. K., Bliha, M., DeLuca, J., Frauhiger, A., & Lamichhane-Khadka, R. (2019, January/February). Bacteria on the soles of patient-issued nonskid slipper socks: An overlooked pathogen spread threat? Orthopedic Nursing, 38(1), 33-40. https://doi.org/10.1097/nor.0000000000000516 ↵
- “Dermatitis2015.jpg” by James Heilman, MD is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0 ↵

Test your knowledge using this NCLEX Next Generation-style Case Study. You may reset and resubmit your answers to this question an unlimited number of times.[1]

Test your knowledge using this NCLEX Next Generation-style Case Study. You may reset and resubmit your answers to this question an unlimited number of times.[2]
Acuity-based staffing: A patient assignment model that takes into account the level of patient care required based on the severity of a patient’s illness or condition.
Affordable Care Act (ACA): Legislation enacted in 2010 to increase consumers' access to health care coverage and protect them from insurance practices that restrict care or significantly increase the cost of care.
Budget: An estimate of revenue and expenses over a specified period of time, usually over a year.
Capital budgets: Budgets used to plan investments and upgrades to tangible assets that lose or gain value over time. Capital is something that can be touched, such as buildings or computers.
Co-pay: A flat fee the consumer pays at the time of receiving a health care service as a part of their health care plan.
Deductible: The amount of money a consumer pays for health care before their insurance plan pays anything. These amounts generally apply per person per calendar year.
Economics: The study of how society makes decisions about its limited resources.
Evidence Based Practice (EBP): A lifelong problem-solving approach that integrates the best evidence from well-designed research studies and evidence-based theories; clinical expertise and evidence from assessment of the health care consumer’s history and condition, as well as health care resources; and patient, family, group, community, and population preferences and values.
Extrinsic factors: External elements that impact health care costs.
Floating: An agency strategy that asks nurses to temporarily work on a different unit to help cover a short-staffed shift.
Health care disparity: Differences in access to health care and insurance coverage.
Health disparities: Differences in health outcomes that result from social determinants of health (SDOH).
Intrinsic factors: Factors that are inherent to the characteristics and needs of the population.
Mandatory overtime: A requirement by agencies for nurses to stay and care for patients beyond their scheduled shift when short staffing occurs.
Medicaid: A joint federal and state program covering groups of eligible individuals, such as low-income families, qualified pregnant women and children, and individuals receiving Supplemental Security Income (SSI). States may choose to cover additional groups, such as individuals receiving home and community-based services and children in foster care who are not otherwise eligible.
Medicare: A federal health insurance program used by people aged 65 and older, younger individuals with permanent disabilities, and people with end-stage renal disease requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Off with benefits: An agency staffing strategy when a nurse is not needed for their scheduled shift. The nurse does not typically receive an hourly wage and is not expected to report to work, but they still accrue benefits such as insurance and paid time off.
On call: An agency staffing strategy when a nurse is not immediately needed for their scheduled shift. They may have options to stay at work and complete work-related education or stay home.
Operating budgets: Budgets including personnel costs and annual facility operating costs.
Pay for Performance: A reimbursement model, also known as value-based payment, that attaches financial incentives based on the performance of health care agencies and providers.
Resource stewardship: Using appropriate resources to plan, provide, and sustain evidence-based nursing services that are safe, effective, financially responsible, and used judiciously.
Social Determinants of Health (SDOH): Conditions in the places where people live, learn, work, and play, such as unstable housing, low income areas, unsafe neighborhoods, or substandard education that affect a wide range of health risks and outcomes.
Team nursing: A common staffing pattern that uses a combination of Registered Nurses (RNs), Licensed Practical/Vocational Nurses (LPN/VNs), and Assistive Personnel (AP) to care for a group of patients.
Acuity-based staffing: A patient assignment model that takes into account the level of patient care required based on the severity of a patient’s illness or condition.
Affordable Care Act (ACA): Legislation enacted in 2010 to increase consumers' access to health care coverage and protect them from insurance practices that restrict care or significantly increase the cost of care.
Budget: An estimate of revenue and expenses over a specified period of time, usually over a year.
Capital budgets: Budgets used to plan investments and upgrades to tangible assets that lose or gain value over time. Capital is something that can be touched, such as buildings or computers.
Co-pay: A flat fee the consumer pays at the time of receiving a health care service as a part of their health care plan.
Deductible: The amount of money a consumer pays for health care before their insurance plan pays anything. These amounts generally apply per person per calendar year.
Economics: The study of how society makes decisions about its limited resources.
Evidence Based Practice (EBP): A lifelong problem-solving approach that integrates the best evidence from well-designed research studies and evidence-based theories; clinical expertise and evidence from assessment of the health care consumer’s history and condition, as well as health care resources; and patient, family, group, community, and population preferences and values.
Extrinsic factors: External elements that impact health care costs.
Floating: An agency strategy that asks nurses to temporarily work on a different unit to help cover a short-staffed shift.
Health care disparity: Differences in access to health care and insurance coverage.
Health disparities: Differences in health outcomes that result from social determinants of health (SDOH).
Intrinsic factors: Factors that are inherent to the characteristics and needs of the population.
Mandatory overtime: A requirement by agencies for nurses to stay and care for patients beyond their scheduled shift when short staffing occurs.
Medicaid: A joint federal and state program covering groups of eligible individuals, such as low-income families, qualified pregnant women and children, and individuals receiving Supplemental Security Income (SSI). States may choose to cover additional groups, such as individuals receiving home and community-based services and children in foster care who are not otherwise eligible.
Medicare: A federal health insurance program used by people aged 65 and older, younger individuals with permanent disabilities, and people with end-stage renal disease requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Off with benefits: An agency staffing strategy when a nurse is not needed for their scheduled shift. The nurse does not typically receive an hourly wage and is not expected to report to work, but they still accrue benefits such as insurance and paid time off.
On call: An agency staffing strategy when a nurse is not immediately needed for their scheduled shift. They may have options to stay at work and complete work-related education or stay home.
Operating budgets: Budgets including personnel costs and annual facility operating costs.
Pay for Performance: A reimbursement model, also known as value-based payment, that attaches financial incentives based on the performance of health care agencies and providers.
Resource stewardship: Using appropriate resources to plan, provide, and sustain evidence-based nursing services that are safe, effective, financially responsible, and used judiciously.
Social Determinants of Health (SDOH): Conditions in the places where people live, learn, work, and play, such as unstable housing, low income areas, unsafe neighborhoods, or substandard education that affect a wide range of health risks and outcomes.
Team nursing: A common staffing pattern that uses a combination of Registered Nurses (RNs), Licensed Practical/Vocational Nurses (LPN/VNs), and Assistive Personnel (AP) to care for a group of patients.

