13.4 Musculoskeletal Assessment
Open Resources for Nursing (Open RN)
Now that you reviewed the anatomy of the musculoskeletal system and common musculoskeletal conditions, let’s discuss the components of a routine nursing assessment.
Subjective Assessment
Collect subjective data from the patient and pay particular attention to what the patient is reporting about current symptoms, as well as past history of musculoskeletal injuries and disease. Information during the subjective assessment should be compared to expectations for the patient’s age group or that patient’s baseline. For example, an older patient may have chronic limited range of motion in the knee due to osteoarthritis, whereas a child may have new, limited range of motion due to a knee sprain that occurred during a sports activity.
If the patient reports a current symptom, use the PQRSTU method described in the “Health History” chapter to obtain more information about this chief complaint. If the patient is experiencing acute pain or recent injury, focus on providing pain relief and/or stabilization of the injury prior to proceeding with the interview. Use information obtained during the subjective assessment to guide your physical examination. Sample focused interview questions to include during a subjective assessment of the musculoskeletal system are contained in Table 13.4a. The first question of the musculoskeletal interview is based on the six most common symptoms related to musculoskeletal disease.[1]
Table 13.4a Focused Interview Questions Related to the Musculoskeletal System
| Interview Questions | Follow-up |
|---|---|
| Are you experiencing any current musculoskeletal symptoms such as muscle weakness, pain, swelling, redness, warmth, or stiffness? | Describe your concern today.
How is it affecting your ability to complete daily activities? P: Does anything bring on the symptom such as activity, weight-bearing, or rest? If activity brings on the symptom, how much activity is required to bring on the symptom(s)? Does it occur at a certain time of day? Is there anything that makes it better or go away? Q: Describe the characteristics of the pain (aching, throbbing, sharp, dull). R: Is the pain localized or does it radiate to another part or area of the body? S: How severe is the pain on a scale of 0-10? T: When did the pain first start? Is it constant or does it come and go? Have you taken anything to relieve the pain? U: What do you think is causing the pain? |
| Have you ever been diagnosed with a chronic musculoskeletal disease such as osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, or rheumatoid arthritis? | Please describe the conditions and treatments. |
| Have you ever been diagnosed with a neurological condition that affected the use of your muscles? | Please describe. |
| Have you had any previous surgeries on your bones or muscles, such as fracture repair or knee or hip surgery? | Please describe. |
| Are you currently taking any medications, herbs, or supplements for your muscles, bones, or the health of your musculoskeletal system? | Please describe. |
| Have you ever had a broken bone, strain, or other injury to a muscle, joint, tendon, or ligament? | Please describe. |
Life Span Considerations
When conducting a subjective interview of children, additional information may be obtained from the parent or legal guardian.
Newborn
- Did your baby experience any trauma during labor and delivery?
- Did the head come first during delivery of your baby? Was the baby in breech position requiring delivery by Caesarean section?
- Were forceps used during delivery?
- Have you been told your infant has a “click” within the hip(s)?
- Do you have any concern with your baby moving any joints, extremities, or neck normally? If so, describe.
Pediatric
- Has your child ever had a broken bone? If so, how was it treated?
- Has your child had any dislocation of a joint?
- Have you noticed any abnormality with your child’s spine, toes, feet, or hands? If so, describe.
- Does your child have any difficulty walking, jumping, or playing? If so, describe.
- Is your child involved in sports or organized physical activities? Do you have any concerns about your child being physically able to perform these activities?
Older Adults
When assessing older adults, it is important to assess their mobility and their ability to perform activities of daily living.
- Do you use any assistive devices such as a brace, cane, walker, or wheelchair?
- Have you fallen or had any near falls in the past few months? If so, was there any injury or did you seek medical care?
- Describe your mobility as of today. Have you noticed any changes in your ability to complete your usual daily activities such as walking, going to the bathroom, bathing, doing laundry, or preparing meals? If so, do you have any assistance available?
Objective Assessment
The purpose of a routine physical exam of the musculoskeletal system by a registered nurse is to assess function and to screen for abnormalities. Most information about function and mobility is gathered during the patient interview, but the nurse also observes the patient’s posture, walking, and movement of their extremities during the physical exam.
During a routine assessment of a patient during inpatient care, a registered nurse typically completes the following musculoskeletal assessments:
- Assess gait
- Inspect the spine
- Observe range of motion of joints
- Inspect muscles and extremities for size and symmetry
- Assess muscle strength
- Palpate extremities for tenderness[2]
While assessing an older adult, keep in mind they may have limited mobility and range of motion due to age-related degeneration of joints and muscle weakness. Be considerate of these limitations and never examine any areas to the point of pain or discomfort. Support the joints and muscles as you assess them to avoid pain or muscle spasm. Compare bilateral sides simultaneously and expect symmetry of structure and function of the corresponding body area.
Inspection
General inspection begins by observing the patient in the standing position for postural abnormalities. Observe their stance and note any abnormal curvature of the spine such as kyphosis, lordosis, or scoliosis. Ask the patient to walk away from you, turn, and walk back toward you while observing their gait and balance.
Ask the patient to sit. Inspect the size and contour of the muscles and joints and if the corresponding parts are symmetrical. Notice the skin over the joints and muscles and observe if there is tenderness, swelling, erythema, deformity, or asymmetry. Observe how the patient moves their extremities and note if there is pain with movement or any limitations in active range of motion (ROM). Active range of motion is the degree of movement the patient can voluntarily achieve in a joint without assistance. See Figures 13.9 and 13.10 as resources for describing joint movement.
Palpation
Palpation is typically done simultaneously during inspection. As you observe, palpate each joint for warmth, swelling, or tenderness. If you observe decreased active range of motion, gently attempt passive range of motion by stabilizing the joint with one hand while using the other hand to gently move the joint to its limit of movement. Passive range of motion is the degree of range of motion demonstrated in a joint when the examiner is providing the movement. You may hear crepitus as the joint moves. Crepitus sounds like a crackling, popping noise that is considered normal as long as it is not associated with pain. As the joint moves, there should not be any reported pain or tenderness.
Assess muscle strength. Muscle strength should be equal bilaterally, and the patient should be able to fully resist an opposing force. Muscle strength varies among people depending on their activity level, genetic predisposition, lifestyle, and history. A common method of evaluating muscle strength is the Medical Research Council Manual Muscle Testing Scale.[3] This method involves testing key muscles from the upper and lower extremities against gravity and the examiner’s resistance and grading the patient’s strength on a 0 to 5 scale. See Box 13.4 for the muscle strength testing scale.
Muscle Strength Scale[4]
0 – No muscle contraction
1 – Trace muscle contraction, such as a twitch
2 – Active movement only when gravity eliminated
3 – Active movement against gravity but not against resistance
4 – Active movement against gravity and some resistance
5 – Active movement against gravity and examiner’s full resistance
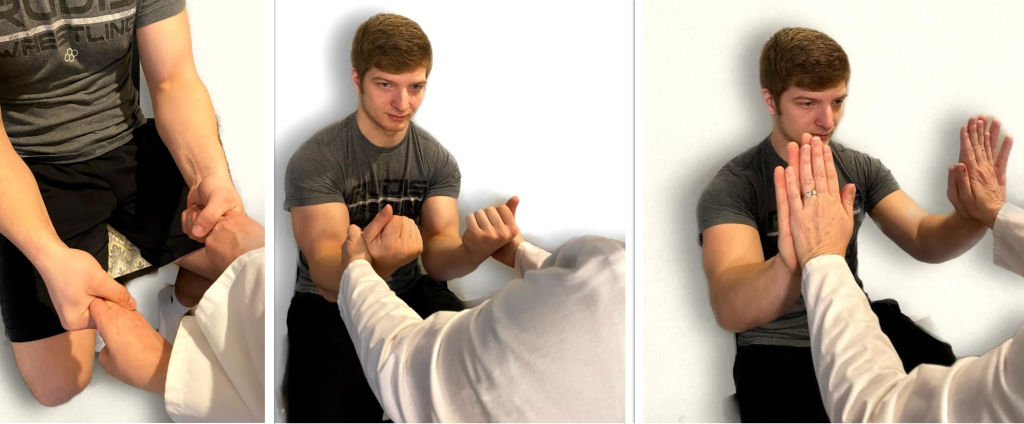
To assess upper extremity strength, first begin by assessing bilateral hand grip strength. Extend your index and second fingers on each hand toward the patient and ask them to squeeze them as tightly as possible. Then, ask the patient to extend their arms with their palms up. As you provide resistance on their forearms, ask the patient to pull their arms towards them. Finally, ask the patient to place their palms against yours and press while you provide resistance. See Figure 13.25[5] for images of a nurse assessing upper extremity strength.
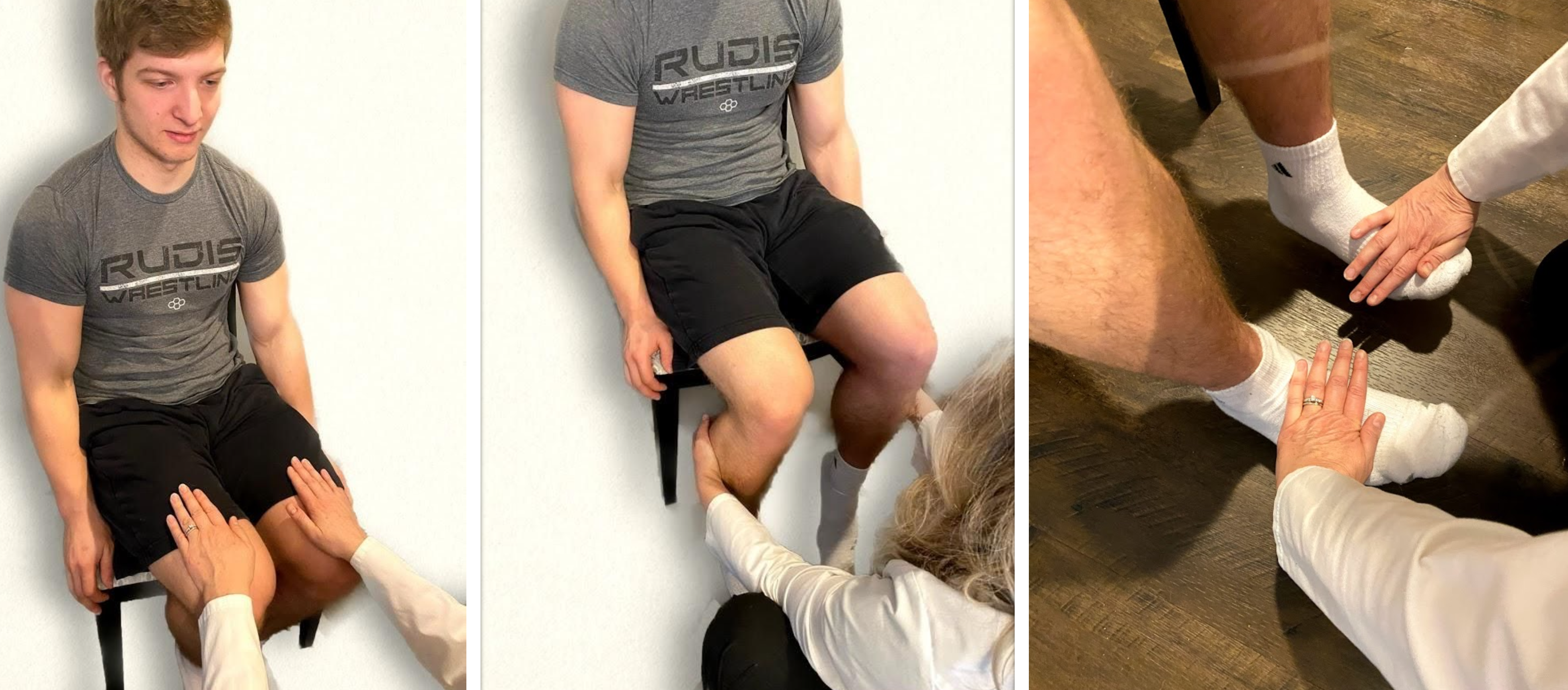
To assess lower extremity strength, perform the following maneuvers with a seated patient. Place your palms on the patient’s thighs and ask them to lift their legs while providing resistance. Secondly, place your hands behind their calves and ask them to pull their legs backwards while you provide resistance. Place your hands on the top of their feet and ask them to pull their feet upwards against your resistance. Finally, place your hands on the soles of their feet and ask them to press downwards while you provide resistance, instructing them to “press downwards like pressing the gas pedal on a car.” See Figure 13.26[6] for images of a nurse assessing lower extremity strength.
To read additional details regarding a full range of motion assessment of the musculoskeletal system, visit the following chapter from Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations. 3rd edition: An Overview of the Musculoskeletal System.
View a supplementary YouTube video on Musculoskeletal Assessment[7]
See Table 13.4b for a comparison of expected versus unexpected findings when assessing the musculoskeletal system.
Table 13.4b Expected Versus Unexpected Findings on Musculoskeletal Assessment
| Assessment | Expected Findings | Unexpected Findings (Document and notify provider if a new finding*) |
|---|---|---|
| Inspection | Erect posture with good balance and normal gait while walking. Joints and muscles are symmetrical with no swelling, redness, or deformity. Active range of motion of all joints without difficulty. No spine curvature from posterior view. | Spinal curvature is present. Poor balance or unsteady gait while walking. Swelling, bruising, erythema, or tenderness over joints or muscles. Deformity of joints. Decreased active range of motion. Contracture or foot drop present. |
| Auscultation | Not applicable | Crepitus associated with pain on movement. |
| Palpation | No palpable tenderness or warmth of joints, bones, or muscles. Muscle strength 5/5 against resistance. | Warmth or tenderness on palpation of joints, bones, or muscles. Decreased passive range of motion. Muscle strength of 3/5 or less. |
| *CRITICAL CONDITIONS to report immediately | Hot, swollen, painful joint. Suspected fracture, dislocation, sprain, or strain. |
- Miller, S. B. (1990). An overview of the musculoskeletal system. In Walker, H. K., Hall, W. D., Hurst, J. W. (Eds.), Clinical methods: The history, physical, and laboratory examinations (3rd ed.). Butterworths. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK266/ ↵
- Giddens, J. F. (2007). A survey of physical examination techniques performed by RNs: Lessons for nursing education. Journal of Nursing Education, 46(2), 83-87. https://doi.org/10.3928/01484834-20070201-09 ↵
- This work is a derivative of StatPearls by Naqvi and Sherman and is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
- This work is a derivative of StatPearls by Naqvi and Sherman and is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
- “Neuro Exam image 38.png,” “Neuro Exam image 41.png,” and “Neuro Exam image 39.jpg” by Meredith Pomietlo for Chippewa Valley Technical College are licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
- “Musculoskeletal Exam image 2.png,” “Neuro Exam image 6.png,” and “Musculoskeletal Exam Image 7.png” by Meredith Pomietlo for Chippewa Valley Technical College are licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
- RegisteredNurseRN. (2017, December 22). Upper & lower extremities assessment nursing | Upper, lower extremity examination [Video]. YouTube. All rights reserved. Video used with permission. https://youtu.be/1sKnumpKT_Y ↵
Learning Objectives
- Differentiate the role of leader and manager
- Examine the roles of team members
- Identify steps in the management process and activities that managers perform
- Describe the role of the RN as a leader and change agent
- Discuss effects of power, empowerment, and motivation in leading and managing a nursing team
As a nursing student preparing to graduate, you have spent countless hours on developing clinical skills, analyzing disease processes, creating care plans, and cultivating clinical judgment. In comparison, you have likely spent much less time on developing management and leadership skills. Yet, soon after beginning your first job as a registered nurse, you will become involved in numerous situations requiring nursing leadership and management skills. Some of these situations include the following:
- Prioritizing care for a group of assigned clients
- Collaborating with interprofessional team members regarding client care
- Participating in an interdisciplinary team conference
- Acting as a liaison when establishing community resources for a patient being discharged home
- Serving on a unit committee
- Investigating and implementing a new evidence-based best practice
- Mentoring nursing students
Delivering safe, quality client care often requires registered nurses (RN) to manage care provided by the nursing team. Making assignments, delegating tasks, and supervising nursing team members are essential managerial components of an entry-level staff RN role. As previously discussed, nursing team members include RNs, licensed practical/vocational nurses (LPN/VN), and assistive personnel (AP).[1]
Read more about assigning, delegating, and supervising in the “Delegation and Supervision” chapter.
An RN is expected to demonstrate leadership and management skills in many facets of the role. Nurses manage care for high-acuity patients as they are admitted, transferred, and discharged; coordinate care among a variety of diverse health professionals; advocate for clients’ needs; and manage limited resources with shrinking budgets.[2]
Read more about collaborating and communicating with the interprofessional team; advocating for clients; and admitting, transferring, and discharging clients in the “Collaboration Within the Interprofessional Team” chapter.
An article published in the Online Journal of Issues in Nursing states, "With the growing complexity of healthcare practice environments and pending nurse leader retirements, the development of future nurse leaders is increasingly important."[3] This chapter will explore leadership and management responsibilities of an RN. Leadership styles are introduced, and change theories are discussed as a means for implementing change in the health care system.
Learning Objectives
- Differentiate the role of leader and manager
- Examine the roles of team members
- Identify steps in the management process and activities that managers perform
- Describe the role of the RN as a leader and change agent
- Discuss effects of power, empowerment, and motivation in leading and managing a nursing team
As a nursing student preparing to graduate, you have spent countless hours on developing clinical skills, analyzing disease processes, creating care plans, and cultivating clinical judgment. In comparison, you have likely spent much less time on developing management and leadership skills. Yet, soon after beginning your first job as a registered nurse, you will become involved in numerous situations requiring nursing leadership and management skills. Some of these situations include the following:
- Prioritizing care for a group of assigned clients
- Collaborating with interprofessional team members regarding client care
- Participating in an interdisciplinary team conference
- Acting as a liaison when establishing community resources for a patient being discharged home
- Serving on a unit committee
- Investigating and implementing a new evidence-based best practice
- Mentoring nursing students
Delivering safe, quality client care often requires registered nurses (RN) to manage care provided by the nursing team. Making assignments, delegating tasks, and supervising nursing team members are essential managerial components of an entry-level staff RN role. As previously discussed, nursing team members include RNs, licensed practical/vocational nurses (LPN/VN), and assistive personnel (AP).[4]
Read more about assigning, delegating, and supervising in the “Delegation and Supervision” chapter.
An RN is expected to demonstrate leadership and management skills in many facets of the role. Nurses manage care for high-acuity patients as they are admitted, transferred, and discharged; coordinate care among a variety of diverse health professionals; advocate for clients’ needs; and manage limited resources with shrinking budgets.[5]
Read more about collaborating and communicating with the interprofessional team; advocating for clients; and admitting, transferring, and discharging clients in the “Collaboration Within the Interprofessional Team” chapter.
An article published in the Online Journal of Issues in Nursing states, "With the growing complexity of healthcare practice environments and pending nurse leader retirements, the development of future nurse leaders is increasingly important."[6] This chapter will explore leadership and management responsibilities of an RN. Leadership styles are introduced, and change theories are discussed as a means for implementing change in the health care system.

