IV Therapy Site Assessment & Complications
Open Resources for Nursing (Open RN)
Catheter Size and Type Selection
Peripheral IV catheters are available in a variety of sizes, most commonly ranging from 14 gauge to 26 gauge. Note that the lower the gauge size, the wider the diameter of the catheter, with 14-gauge catheters allowing for the greatest flow rate.[1] Catheter sizes are color coded to allow for easy identification of the catheter size after a vein is accessed. See Figure 23.12[2] for colors associated with IV catheter sizes and their associated flow rates.

Nurses must consider the purpose for venous access, along with assessment of the patient’s vessel size, when selecting an IV catheter to attempt cannulation. The smallest IV catheter should be selected that will accommodate the prescribed therapy and patient need.[3]
Catheters with a smaller gauge (i.e., larger diameter) permit infusion of viscous fluids, such as blood products, at a faster rate with decreased opportunity for catheter occlusion.[4] Additionally, an appropriately sized catheter also allows for adequate blood flow around the catheter itself. The most common IV catheter size for adult patients is 18- or 20-gauge catheters. However, frail elderly patients and children have smaller vasculature, so a 22-gauge catheter is often preferred.
There are different manufacturer brands of IV catheters, but all include a beveled hollow needle, a flashback chamber in which blood can be visualized when entering the vein, and a flexible catheter that is left in the vein after the catheter has been threaded into the vein and the needle removed.
IV insertion equipment varies among institutions, but common types include shielded IV catheters or winged (i.e., “butterfly”) devices. Variation is often related to the presence of a stabilizing device at the site of insertion, as well as the presence of short extension tubing. For shielded catheter types, the stabilizing device and extension tubing are typically added to the catheter itself and not included with the cannulation needle. See Figure 23.13[5] for an image of shielded IV catheters.
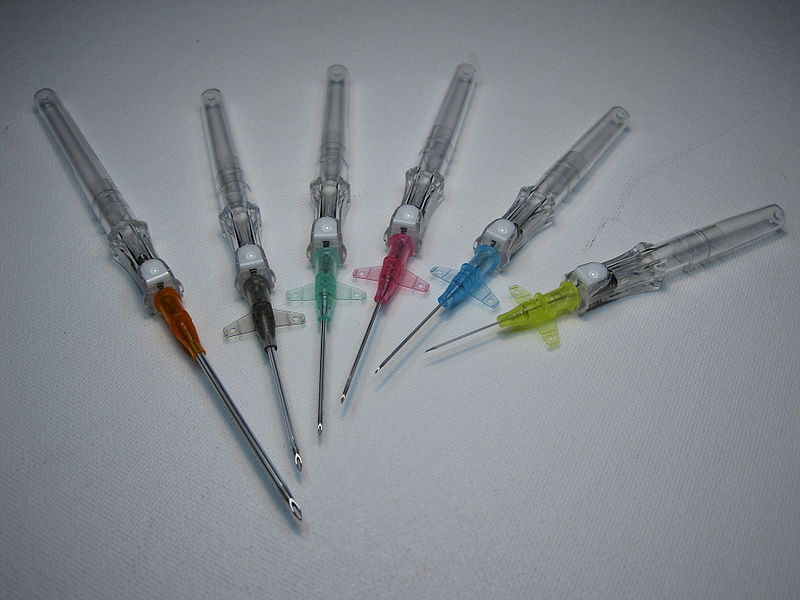
Nurses must ensure the selected size and type of IV catheter are appropriate for the procedure or infusion that is ordered because not all peripheral IV catheters are suitable for all procedures. For example, if a procedure requires the infusion of contrast dye, a specific size infusion port is required.
Despite the wide variation in catheter equipment that is available, there has been significant focus among manufacturers regarding the need for safety equipment during venipuncture. Many devices utilize mechanisms to self-contain needles within a plastic sheath after withdrawal from the patient. These devices can be activated through a button in the devices or a manual trigger initiated by the individual attempting cannulation. Regardless of the type of safety lock, it is important to utilize the equipment as intended and never attempt to disable or override the mechanism. These mechanisms are important to help prevent accidental needlesticks or injury with a contaminated needle after it has been removed from the patient. Additionally, after cannulation is attempted, the individual who attempted cannulation is responsible for ensuring all needles are disposed of in a sharps container. It is good practice to be aware of how many sharps were brought into the room, opened, and disposed. This helps to ensure that any needles are not inadvertently left in a patient’s bed, tray table, floor, etc. Nurses must be familiar with the equipment used at the health care facility and receive orientation on the specific mechanics related to the equipment and safety practices.
Initiating Peripheral IV Access
The steps for initiating peripheral IV access are described in the Open RN Nursing Advanced Skills “Perform IV Insertion and IV Removal” checklist in Chapter 1.
Monitoring for Potential Complications
Several potential complications may arise from peripheral intravenous therapy. It is the responsibility of the nurse to prevent, assess, and manage signs and symptoms of complications. Complications can be categorized as local or systemic. See Table 23.4a for potential local complications of peripheral IV therapy.
Table 23.4a Local Complications of Peripheral IV Therapy[6],[7]
| Complications | Potential Causes and Prevention | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Phlebitis: The inflammation of the vein’s inner lining, the tunica intima. Clinical indications are localized redness, pain, heat, purulent drainage, and swelling that can track up the vein leading to a palpable venous cord. | Mechanical causes: Inflammation of the vein’s inner lining can be caused by the cannula rubbing and irritating the vein. To prevent mechanical inflammation, choose the smallest outer diameter of a catheter for therapy, secure the catheter with securement technology, avoid areas of flexion, and stabilize the joint as needed.[8]
Chemical causes: Inflammation of the vein’s inner lining can be caused by medications or fluids with high alkaline, acidic, or hypertonic qualities. To avoid chemical phlebitis, follow the parenteral drug therapy guidelines in a drug reference resource for administering IV medications, including the appropriate amount of solution and rate of infusion. Infectious causes: May be related to emergent VAD insertions, poor aseptic technique, or contaminated dressings. |
Chemical phlebitis: Evaluate infusion therapy and the need for different vascular access, different medication, slower rate of infusion, or more dilute infusate. If indicated, remove the Vascular Access Device (VAD).[9]
Transient mechanical phlebitis: May be treatable by stabilizing the catheter, applying heat, elevating limb, and providing analgesics as needed. Consider requesting other pharmacologic interventions such as anti-inflammatory agents if needed. Monitor site for 24 hours post-insertion, and if signs and symptoms persist, remove the catheter.[10] Infectious phlebitis: If purulent drainage is present or infection is suspected, remove the catheter and obtain a culture of the purulent drainage and catheter tip. Monitor for signs of systemic infection.[11] |
| Infiltration: A condition that occurs when a nonvesicant solution is inadvertently administered into surrounding tissue. Signs and symptoms include pain, swelling, redness, the skin surrounding the insertion site is cool to touch, there is a change in the quality or flow of IV, the skin is tight around the IV site, IV fluid is leaking from IV site, or there are frequent alarms on the IV pump. | Infiltration is one of the most common complications in infusion therapy involving an IV catheter.[12] For this reason, the patency of an IV site must always be checked before administering IV push medications.
Infiltration can be caused by piercing the vein, excessive patient movement, a dislodged or incorrectly placed IV catheter, or too rapid infusion of fluids or medications into a fragile vein. Always secure a peripheral IV catheter with tape or a stabilization device to avoid accidental dislodgement. Avoid sites that are areas of flexion. |
Stop the infusion and remove the cannula. Follow agency policy related to infiltration. |
| Extravasation: A condition that occurs when vesicant (an irritating solution or medication) is administered and inadvertently leaks into surrounding tissue and causes damage. It is characterized by the same signs and symptoms as infiltration but also includes burning, stinging, redness, blistering, or necrosis of the tissue. | Extravasation has the same potential causes of infiltration but with worse consequences because of the effects of vesicants. Extravasation can result in severe tissue injury and death (necrosis). For this reason, known vesicant medications should be administered via central lines. | Stop the infusion. Detach all administration sets and aspirate from the catheter hub prior to removing the catheter to remove vesicant medication from the catheter lumen and as much as possible from the subcutaneous tissue.[13]
Follow agency policy regarding extravasation of specific medications. For example, toxic medications have a specific treatment plan. |
| Hemorrhage: Bleeding from the IV access site. | Bleeding occurs when the IV catheter becomes dislodged. | If dislodgement occurs, apply pressure with gauze to the site until the bleeding stops and then apply a sterile transparent dressing. |
| Local infection: Infection at the site is indicated by purulent drainage, typically two to three days after an IV site is started. | Local infection is often caused by nonadherence to aseptic technique during IV initiation or IV maintenance or the dressing becomes contaminated or non-intact over the access site. | Remove the cannula and clean the site using sterile technique. If infection is suspected, remove the catheter and obtain a culture of the purulent drainage and catheter tip. Monitor for signs of systemic infection. |
| Nerve injury[14] | Paresthesia-type pain occurring during venipuncture or during an indwelling IV catheter can indicate nerve injury. | Immediately remove the cannula, notify the provider, and document findings in the chart. |
In addition to local complications that can occur at the site of IV insertion, there are many systemic complications that nurses must monitor for when initiating peripheral IV access, as well as monitoring a patient receiving IV therapy. See Table 23.4b for a list of systemic complications, signs, symptoms, and treatment.
Table 23.4b Systemic Complications of Peripheral IV Therapy[15]
| Complication | Signs, Symptoms, and Treatment |
|---|---|
| Pulmonary Edema | Pulmonary edema, also known as fluid overload or circulatory overload, is a condition caused by excess fluid accumulation in the lungs due to excessive fluid in the circulatory system. It is characterized by decreased oxygen saturation; increased respiratory rate; fine or coarse crackles in the lung bases; restlessness; breathlessness; dyspnea; and coughing up pink, frothy sputum. Pulmonary edema requires prompt medical attention and treatment. If pulmonary edema is suspected, raise the head of the bed, apply oxygen, take vital signs, complete a cardiovascular assessment, and immediately notify the provider. |
| Air Embolism | An air embolism refers to the presence of air in the cardiovascular system. It occurs when air is introduced into the venous system and travels to the right ventricle and/or pulmonary circulation. Air embolisms can occur during catheter insertion, changing IV bags, adding secondary medication administration, and catheter removal. Inadvertent administration of 10 mL of air can have serious and fatal consequences. However, small air bubbles are tolerated by most patients. Signs and symptoms of an air embolism include sudden shortness of breath, continued coughing, breathlessness, shoulder or neck pain, agitation, feeling of impending doom, light-headedness, hypotension, wheezing, increased heart rate, altered mental status, and jugular venous distension.
If an air embolism is suspected, occlude the source of air entry. Place the patient in a Trendelenburg position on their left side (if not contraindicated), apply oxygen at 100%, obtain vital signs, and immediately notify the provider. To prevent air embolisms, perform the following steps when administering IV therapy: ensure the drip chamber is one-third to one-half filled, remove all air from the IV tubing by priming it prior to attaching it to the patient, use precautions when changing IV bags or adding secondary medication bags, ensure all IV connections are tight, and ensure clamps are used when the IV system is not in use. |
| Catheter Embolism | A catheter embolism occurs when a small part of the cannula breaks off and flows into the vascular system. When removing a peripheral IV cannula, inspect the catheter tip to ensure the end is intact. Notify the provider immediately if the catheter tip is not intact when it is removed. |
| Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection (CR-BSI) | Catheter-related bloodstream infection (CR-BSI) is caused by microorganisms introduced into the bloodstream through the puncture site, the hub, or contaminated IV tubing or IV solution, leading to bacteremia or sepsis. A CR-BSI is a hospital-acquired preventable infection and considered an adverse event. A CR-BSI is diagnosed when infection occurs with one positive blood culture in a patient with a vascular device (or a patient who had a vascular device within 48 hours before the infection) with no apparent source for the infection other than the vascular access device. Treatment for CR-BSI is IV antibiotic therapy.
To prevent CR-BSI, it is vital to perform hand hygiene prior to care and maintenance of an IV system and to use strict aseptic technique for care and maintenance of all IV therapy procedures. |
Media Attributions
- 800px-Color-coding_of_IV_cannulas
- 800px-IV_Catheters_9
- This work is a derivative of StatPearls by Beecham & Tackling and is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
- “Color-coding_of_IV_cannulas.jpg” by Dr.Vijaya Chandar is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0 ↵
- Gorski, L. A., Hadaway, L., Hagle, M. E., Broadhurst, D., Clare, S., Kleidon, T., Meyer, B. M., Nickel, B., Rowley, S., Sharp, E., & Alexander, M. A. (2021). Infusion therapy standards of practice. Journal of Infusion Nursing, 44(Suppl 1S), S1–S224. https://doi: 10.1097/NAN.0000000000000396.org ↵
- This work is a derivative of StatPearls by Beecham & Tackling and is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
- “IV_Catheters_(9).JPG” by Intropin is licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 ↵
- This work is a derivative of Clinical Procedures for Safer Patient Care by British Columbia Institute of Technology and is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
- Simin, D., Milutinović, D., Turkulov, V., & Brkić, S. (2018). Incidence, severity and risk factors of peripheral intravenous cannula‐induced complications: An observational prospective study. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 28(9-10), 1585-1599. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.14760 ↵
- Gorski, L. A., Hadaway, L., Hagle, M. E., Broadhurst, D., Clare, S., Kleidon, T., Meyer, B. M., Nickel, B., Rowley, S., Sharp, E., & Alexander, M. A. (2021). Infusion therapy standards of practice. Journal of Infusion Nursing, 44(Suppl 1S), S1–S224. https://doi: 10.1097/NAN.0000000000000396.org ↵
- Gorski, L. A., Hadaway, L., Hagle, M. E., Broadhurst, D., Clare, S., Kleidon, T., Meyer, B. M., Nickel, B., Rowley, S., Sharp, E., & Alexander, M. A. (2021). Infusion therapy standards of practice. Journal of Infusion Nursing, 44(Suppl 1S), S1–S224. https://doi: 10.1097/NAN.0000000000000396.org ↵
- Gorski, L. A., Hadaway, L., Hagle, M. E., Broadhurst, D., Clare, S., Kleidon, T., Meyer, B. M., Nickel, B., Rowley, S., Sharp, E., & Alexander, M. A. (2021). Infusion therapy standards of practice. Journal of Infusion Nursing, 44(Suppl 1S), S1–S224. https://doi: 10.1097/NAN.0000000000000396.org ↵
- Gorski, L. A., Hadaway, L., Hagle, M. E., Broadhurst, D., Clare, S., Kleidon, T., Meyer, B. M., Nickel, B., Rowley, S., Sharp, E., & Alexander, M. A. (2021). Infusion therapy standards of practice. Journal of Infusion Nursing, 44(Suppl 1S), S1–S224. https://doi: 10.1097/NAN.0000000000000396.org ↵
- Wang, J., Li, M. M., Zhou, L. P., Xie, R. H., Pakhale, S., Krewski, D., & Wen, S. W. (2022). Treatment for grade 4 peripheral intravenous infiltration with type 3 skin tears: A case report and literature review. International Wound Journal, 19(1), 222–229. https://doi.org/10.1111/iwj.13624 ↵
- Gorski, L. A., Hadaway, L., Hagle, M. E., Broadhurst, D., Clare, S., Kleidon, T., Meyer, B. M., Nickel, B., Rowley, S., Sharp, E., & Alexander, M. A. (2021). Infusion therapy standards of practice. Journal of Infusion Nursing, 44(Suppl 1S), S1–S224. https://doi: 10.1097/NAN.0000000000000396.org ↵
- Gorski, L. A., Hadaway, L., Hagle, M. E., Broadhurst, D., Clare, S., Kleidon, T., Meyer, B. M., Nickel, B., Rowley, S., Sharp, E., & Alexander, M. A. (2021). Infusion therapy standards of practice. Journal of Infusion Nursing, 44(Suppl 1S), S1–S224. https://doi: 10.1097/NAN.0000000000000396.org ↵
- This work is a derivative of Clinical Procedures for Safer Patient Care by British Columbia Institute of Technology and is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
This textbook discusses professional and management concepts related to the role of a registered nurse (RN) as defined by the American Nurses Association (ANA). The ANA publishes two resources that set standards and guide professional nursing practice in the United States: The Code of Ethics for Nurses With Interpretive Statements and Nursing: Scope and Standards of Practice. The Code of Ethics for Nurses With Interpretive Statements establishes an ethical framework for nursing practice across all roles, levels, and settings and is discussed in greater detail in the “Ethical Practice” chapter of this book. The Nursing: Scope and Standards of Practice resource defines the “who, what, where, when, why, and how of nursing” and sets the standards for practice that all registered nurses are expected to perform competently.[1]
The ANA defines the “who” of nursing practice as the nurses who have been educated, titled, and maintain active licensure to practice nursing. The “what” of nursing is the recently revised ANA definition of nursing: “Nursing integrates the art and science of caring and focuses on the protection, promotion, and optimization of health and human functioning; prevention of illness and injury; facilitation of healing; and alleviation of suffering through compassionate presence. Nursing is the diagnosis and treatment of human responses and advocacy in the care of individuals, families, groups, communities, and populations in recognition of the connection of all humanity.”[2] Simply put, nurses treat human responses to health problems and life processes and advocate for the care of others.
Nursing practice occurs “when'' there is a need for nursing knowledge, wisdom, caring, leadership, practice, or education, anytime, anywhere. Nursing practice occurs in any environment “where'' there is a health care consumer in need of care, information, or advocacy. The “why” of nursing practice is described as nursing’s response to the changing needs of society to achieve positive health care consumer outcomes in keeping with nursing’s social contract and obligation to society. The “how” of nursing practice is defined as the ways, means, methods, and manners that nurses use to practice professionally.[3] The “how” of nursing, also referred to as a nurse’s “scope and standards of practice,” is further defined by each state’s Nurse Practice Act; agency policies, procedures, and protocols; and federal regulations and ANA’s Standards of Practice.
State Boards of Nursing and Nurse Practice Acts
RNs must legally follow regulations set by the Nurse Practice Act by the state in which they are caring for patients with their nursing license. The Board of Nursing is the state-specific licensing and regulatory body that sets standards for safe nursing care and issues nursing licenses to qualified candidates based on the Nurse Practice Act. The Nurse Practice Act is enacted by that state’s legislature and defines the scope of nursing practice and establishes regulations for nursing practice within that state. If nurses do not follow the standards and scope of practice set forth by the Nurse Practice Act, they may be disciplined by the Board of Nursing in the form of reprimand, probation, suspension, or revocation of their nursing license. Investigations and discipline actions are reportable among states participating in the Nurse Licensure Compact (that allows nurses to practice across state lines) or when a nurse applies for licensure in a different state. The scope and standards of practice set forth in the Nurse Practice Act can also be used as evidence if a nurse is sued for malpractice.
Find your state's Nurse Practice Act on the National Council of State Board of Nursing (NCSBN) website.
Read more about malpractice and protecting your nursing license in the “Legal Implications” chapter of this book.
Agency Policies, Procedures, and Protocols
In addition to practicing according to the Nurse Practice Act in the state they are employed, nurses must also practice according to agency policies, procedures, and protocols.
A policy is an expected course of action set by an agency. For example, hospitals set a policy requiring a thorough skin assessment to be completed when a patient is admitted and then reassessed and documented daily.
Agencies also establish their own set of procedures. A procedure is the method or defined steps for completing a task. For example, each agency has specific procedural steps for inserting a urinary catheter.
A protocol is a detailed, written plan for performing a regimen of therapy. For example, agencies typically establish a hypoglycemia protocol that nurses can independently and quickly implement when a patient’s blood sugar falls below a specific number without first calling a provider. A hypoglycemia protocol typically includes actions such as providing orange juice and rechecking the blood sugar and then reporting the incident to the provider.
Agency-specific policies, procedures, and protocols supersede the information taught in nursing school, and nurses can be held legally liable if they don’t follow them. It is vital for nurses to review and follow current agency-specific procedures, policies, and protocols while also practicing according to that state's nursing scope of practice. Malpractice cases have occurred when a nurse was asked by their employer to do something outside their legal scope of practice, impacting their nursing license. It is up to you to protect your nursing license and follow the Nurse Practice Act when providing patient care. If you have a concern about an agency’s policy, procedure, or protocol, follow the agency’s chain of command to report your concern.
Federal Regulations
Nursing practice is impacted by regulations enacted by federal agencies. Two examples of federal agencies setting standards of care are The Joint Commission and the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
The Joint Commission accredits and certifies over 20,000 health care organizations in the United States. The Joint Commission’s standards help health care organizations measure, assess, and improve performance on functions that are essential to providing safe, high-quality care. The standards are updated regularly to reflect the rapid advances in health care and address topics such as patient rights and education, infection control, medication management, and prevention of medical errors. The annual National Patient Safety Goals are also set by The Joint Commission after reviewing emerging patient safety issues.[4]
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is an example of another federal agency that establishes regulations affecting nursing care. CMS is a part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) that administers the Medicare program and works in partnership with state governments to administer Medicaid. The CMS establishes and enforces regulations to protect patient safety in hospitals that receive Medicare and Medicaid funding. For example, one CMS regulation often referred to as “checking the rights of medication administration” requires nurses to confirm specific information several times before medication is administered to a patient.[5]
Standards of Practice
The ANA defines Standards of Professional Nursing Practice as “authoritative statements of the actions and behaviors that all registered nurses, regardless of role, population, specialty, and setting, are expected to perform competently.”[6] These standards are classified into two categories: Standards of Practice and Standards of Professional Performance.
The ANA’s Standards of Practice describe a competent level of nursing practice as demonstrated by the critical thinking model known as the nursing process. The nursing process includes the components of assessment, diagnosis, outcomes identification, planning, implementation, and evaluation and forms the foundation of the nurse’s decision-making, practice, and provision of care.[7]
Read more information about the nursing process in the “Nursing Process” chapter of Open RN Nursing Fundamentals, 2e.[8]
The ANA’s Standards of Professional Performance “describe a competent level of behavior in the professional role, including activities related to ethics, advocacy, respectful and equitable practice, communication, collaboration, leadership, education, scholarly inquiry, quality of practice, professional practice evaluation, resource stewardship, and environmental health. All registered nurses are expected to engage in professional role activities, including leadership, reflective of their education, position, and role.”[9] This book discusses content related to these professional practice standards. Each professional practice standard is defined in the following sections with information provided to related content in this book and the Open RN Nursing Fundamentals, 2e textbook.[10]
Ethics
The ANA’s Ethics standard states, “The registered nurse integrates ethics in all aspects of practice.”[11]
Read about ethical nursing practice in the “Ethical Practice” chapter of this book.
Advocacy
The ANA’s Advocacy standard states, “The registered nurse demonstrates advocacy in all roles and settings.”[12]
Read about nurse advocacy in the “Advocacy” chapter of this book.
Respectful and Equitable Practice
The ANA’s Respectful and Equitable Practice standard states, “The registered nurse practices with cultural humility and inclusiveness.”
Read about cultural humility and culturally responsive care in the “Diverse Patients” chapter in Open RN Nursing Fundamentals, 2e.[13]
Communication
The ANA’s Communication standard states, “The registered nurse communicates effectively in all areas of professional practice.”[14]
Read about communicating with clients and team members in the “Communication” chapter in Open RN Nursing Fundamentals, 2e.[15]
Read about interprofessional communication strategies that promote patient safety in the “Collaboration Within the Interprofessional Team” chapter of this book.
Collaboration
The ANA’s Collaboration standard states, “The registered nurse collaborates with the health care consumer and other key stakeholders.”[16]
Read about strategies to enhance the performance of the interprofessional team and manage conflict in the “Collaboration Within the Interprofessional Team” chapter of this book.
Leadership
The ANA’s Leadership standard states, “The registered nurse leads within the profession and practice setting.”[17]
Read about leadership, management, and implementing change in the “Leadership and Management” chapter of this book.
Read about assigning, delegating, and supervising patient care in the “Delegation and Supervision” chapter of this book.
Read about tools for prioritizing patient care and managing resources for the nursing team in the “Prioritization” chapter of this book.
Education
The ANA’s Education standard states, “The registered nurse seeks knowledge and competence that reflects current nursing practice and promotes futuristic thinking.”[18]
Read about professional development and specialty certification in the “Preparation for the RN Role” chapter of this book.
Scholarly Inquiry
The ANA’s Scholarly Inquiry standard states, “The registered nurse integrates scholarship, evidence, and research findings into practice.”[19]
Read about integrating evidence-based practice into one’s nursing practice in the “Quality and Evidence-Based Practice” chapter of this book.
Quality of Practice
The ANA’s Quality of Practice standard states, “The nurse contributes to quality nursing practice.”[20]
Read about improving quality patient care and participating in quality improvement initiatives in the “Quality and Evidence-Based Practice” chapter of this book.
Professional Practice Evaluation
The ANA’s Professional Practice Evaluation standard states, “The registered nurse evaluates one’s own and others’ nursing practice.”[21]
Read about nursing practice within the legal framework of health care, negligence, malpractice, and protecting your nursing license in the “Legal Implications” chapter of this book.
Read about reviewing the interprofessional team’s performance, providing constructive feedback, and advocating for patient safety with assertive statements in the “Collaboration Within the Interprofessional Team” chapter of this book.
Resource Stewardship
The ANA’s Resource Stewardship standard states, “The registered nurse utilizes appropriate resources to plan, provide, and sustain evidence-based nursing services that are safe, effective, financially responsible, and used judiciously.”[22]
Read more about health care funding, reimbursement models, budgets and staffing, and resource stewardship in the “Health Care Economics” chapter of this book.
Environmental Health
The ANA’s Environmental Health standard states, “The registered nurse practices in a manner that advances environmental safety and health.”[23]
Read about promoting workplace safety for nurses in the “Safety” chapter in Open RN Nursing Fundamentals, 2e.[24]
Read about fostering a professional environment that does not tolerate abusive behaviors in the “Collaboration Within the Interprofessional Team” chapter of this book.
Read about addressing the impacts of social determinants of health in the “Advocacy” chapter of this book.
This textbook discusses professional and management concepts related to the role of a registered nurse (RN) as defined by the American Nurses Association (ANA). The ANA publishes two resources that set standards and guide professional nursing practice in the United States: The Code of Ethics for Nurses With Interpretive Statements and Nursing: Scope and Standards of Practice. The Code of Ethics for Nurses With Interpretive Statements establishes an ethical framework for nursing practice across all roles, levels, and settings and is discussed in greater detail in the “Ethical Practice” chapter of this book. The Nursing: Scope and Standards of Practice resource defines the “who, what, where, when, why, and how of nursing” and sets the standards for practice that all registered nurses are expected to perform competently.[25]
The ANA defines the “who” of nursing practice as the nurses who have been educated, titled, and maintain active licensure to practice nursing. The “what” of nursing is the recently revised ANA definition of nursing: “Nursing integrates the art and science of caring and focuses on the protection, promotion, and optimization of health and human functioning; prevention of illness and injury; facilitation of healing; and alleviation of suffering through compassionate presence. Nursing is the diagnosis and treatment of human responses and advocacy in the care of individuals, families, groups, communities, and populations in recognition of the connection of all humanity.”[26] Simply put, nurses treat human responses to health problems and life processes and advocate for the care of others.
Nursing practice occurs “when'' there is a need for nursing knowledge, wisdom, caring, leadership, practice, or education, anytime, anywhere. Nursing practice occurs in any environment “where'' there is a health care consumer in need of care, information, or advocacy. The “why” of nursing practice is described as nursing’s response to the changing needs of society to achieve positive health care consumer outcomes in keeping with nursing’s social contract and obligation to society. The “how” of nursing practice is defined as the ways, means, methods, and manners that nurses use to practice professionally.[27] The “how” of nursing, also referred to as a nurse’s “scope and standards of practice,” is further defined by each state’s Nurse Practice Act; agency policies, procedures, and protocols; and federal regulations and ANA’s Standards of Practice.
State Boards of Nursing and Nurse Practice Acts
RNs must legally follow regulations set by the Nurse Practice Act by the state in which they are caring for patients with their nursing license. The Board of Nursing is the state-specific licensing and regulatory body that sets standards for safe nursing care and issues nursing licenses to qualified candidates based on the Nurse Practice Act. The Nurse Practice Act is enacted by that state’s legislature and defines the scope of nursing practice and establishes regulations for nursing practice within that state. If nurses do not follow the standards and scope of practice set forth by the Nurse Practice Act, they may be disciplined by the Board of Nursing in the form of reprimand, probation, suspension, or revocation of their nursing license. Investigations and discipline actions are reportable among states participating in the Nurse Licensure Compact (that allows nurses to practice across state lines) or when a nurse applies for licensure in a different state. The scope and standards of practice set forth in the Nurse Practice Act can also be used as evidence if a nurse is sued for malpractice.
Find your state's Nurse Practice Act on the National Council of State Board of Nursing (NCSBN) website.
Read more about malpractice and protecting your nursing license in the “Legal Implications” chapter of this book.
Read Wisconsin’s Nurse Practice Act, Standards of Practice for Registered Nurses and Licensed Practical Nurses (Chapter N6) PDF, and Rules of Conduct (Chapter N7) PDF.
Agency Policies, Procedures, and Protocols
In addition to practicing according to the Nurse Practice Act in the state they are employed, nurses must also practice according to agency policies, procedures, and protocols.
A policy is an expected course of action set by an agency. For example, hospitals set a policy requiring a thorough skin assessment to be completed when a patient is admitted and then reassessed and documented daily.
Agencies also establish their own set of procedures. A procedure is the method or defined steps for completing a task. For example, each agency has specific procedural steps for inserting a urinary catheter.
A protocol is a detailed, written plan for performing a regimen of therapy. For example, agencies typically establish a hypoglycemia protocol that nurses can independently and quickly implement when a patient’s blood sugar falls below a specific number without first calling a provider. A hypoglycemia protocol typically includes actions such as providing orange juice and rechecking the blood sugar and then reporting the incident to the provider.
Agency-specific policies, procedures, and protocols supersede the information taught in nursing school, and nurses can be held legally liable if they don’t follow them. It is vital for nurses to review and follow current agency-specific procedures, policies, and protocols while also practicing according to that state's nursing scope of practice. Malpractice cases have occurred when a nurse was asked by their employer to do something outside their legal scope of practice, impacting their nursing license. It is up to you to protect your nursing license and follow the Nurse Practice Act when providing patient care. If you have a concern about an agency’s policy, procedure, or protocol, follow the agency’s chain of command to report your concern.
Federal Regulations
Nursing practice is impacted by regulations enacted by federal agencies. Two examples of federal agencies setting standards of care are The Joint Commission and the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
The Joint Commission accredits and certifies over 20,000 health care organizations in the United States. The Joint Commission’s standards help health care organizations measure, assess, and improve performance on functions that are essential to providing safe, high-quality care. The standards are updated regularly to reflect the rapid advances in health care and address topics such as patient rights and education, infection control, medication management, and prevention of medical errors. The annual National Patient Safety Goals are also set by The Joint Commission after reviewing emerging patient safety issues.[28]
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is an example of another federal agency that establishes regulations affecting nursing care. CMS is a part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) that administers the Medicare program and works in partnership with state governments to administer Medicaid. The CMS establishes and enforces regulations to protect patient safety in hospitals that receive Medicare and Medicaid funding. For example, one CMS regulation often referred to as “checking the rights of medication administration” requires nurses to confirm specific information several times before medication is administered to a patient.[29]
Standards of Practice
The ANA defines Standards of Professional Nursing Practice as “authoritative statements of the actions and behaviors that all registered nurses, regardless of role, population, specialty, and setting, are expected to perform competently.”[30] These standards are classified into two categories: Standards of Practice and Standards of Professional Performance.
The ANA’s Standards of Practice describe a competent level of nursing practice as demonstrated by the critical thinking model known as the nursing process. The nursing process includes the components of assessment, diagnosis, outcomes identification, planning, implementation, and evaluation and forms the foundation of the nurse’s decision-making, practice, and provision of care.[31]
Read more information about the nursing process in the “Nursing Process” chapter of Open RN Nursing Fundamentals, 2e.[32]
The ANA’s Standards of Professional Performance “describe a competent level of behavior in the professional role, including activities related to ethics, advocacy, respectful and equitable practice, communication, collaboration, leadership, education, scholarly inquiry, quality of practice, professional practice evaluation, resource stewardship, and environmental health. All registered nurses are expected to engage in professional role activities, including leadership, reflective of their education, position, and role.”[33] This book discusses content related to these professional practice standards. Each professional practice standard is defined in the following sections with information provided to related content in this book and the Open RN Nursing Fundamentals, 2e textbook.[34]
Ethics
The ANA’s Ethics standard states, “The registered nurse integrates ethics in all aspects of practice.”[35]
Read about ethical nursing practice in the “Ethical Practice” chapter of this book.
Advocacy
The ANA’s Advocacy standard states, “The registered nurse demonstrates advocacy in all roles and settings.”[36]
Read about nurse advocacy in the “Advocacy” chapter of this book.
Respectful and Equitable Practice
The ANA’s Respectful and Equitable Practice standard states, “The registered nurse practices with cultural humility and inclusiveness.”
Read about cultural humility and culturally responsive care in the “Diverse Patients” chapter in Open RN Nursing Fundamentals, 2e.[37]
Communication
The ANA’s Communication standard states, “The registered nurse communicates effectively in all areas of professional practice.”[38]
Read about communicating with clients and team members in the “Communication” chapter in Open RN Nursing Fundamentals, 2e.[39]
Read about interprofessional communication strategies that promote patient safety in the “Collaboration Within the Interprofessional Team” chapter of this book.
Collaboration
The ANA’s Collaboration standard states, “The registered nurse collaborates with the health care consumer and other key stakeholders.”[40]
Read about strategies to enhance the performance of the interprofessional team and manage conflict in the “Collaboration Within the Interprofessional Team” chapter of this book.
Leadership
The ANA’s Leadership standard states, “The registered nurse leads within the profession and practice setting.”[41]
Read about leadership, management, and implementing change in the “Leadership and Management” chapter of this book.
Read about assigning, delegating, and supervising patient care in the “Delegation and Supervision” chapter of this book.
Read about tools for prioritizing patient care and managing resources for the nursing team in the “Prioritization” chapter of this book.
Education
The ANA’s Education standard states, “The registered nurse seeks knowledge and competence that reflects current nursing practice and promotes futuristic thinking.”[42]
Read about professional development and specialty certification in the “Preparation for the RN Role” chapter of this book.
Scholarly Inquiry
The ANA’s Scholarly Inquiry standard states, “The registered nurse integrates scholarship, evidence, and research findings into practice.”[43]
Read about integrating evidence-based practice into one’s nursing practice in the “Quality and Evidence-Based Practice” chapter of this book.
Quality of Practice
The ANA’s Quality of Practice standard states, “The nurse contributes to quality nursing practice.”[44]
Read about improving quality patient care and participating in quality improvement initiatives in the “Quality and Evidence-Based Practice” chapter of this book.
Professional Practice Evaluation
The ANA’s Professional Practice Evaluation standard states, “The registered nurse evaluates one’s own and others’ nursing practice.”[45]
Read about nursing practice within the legal framework of health care, negligence, malpractice, and protecting your nursing license in the “Legal Implications” chapter of this book.
Read about reviewing the interprofessional team’s performance, providing constructive feedback, and advocating for patient safety with assertive statements in the “Collaboration Within the Interprofessional Team” chapter of this book.
Resource Stewardship
The ANA’s Resource Stewardship standard states, “The registered nurse utilizes appropriate resources to plan, provide, and sustain evidence-based nursing services that are safe, effective, financially responsible, and used judiciously.”[46]
Read more about health care funding, reimbursement models, budgets and staffing, and resource stewardship in the “Health Care Economics” chapter of this book.
Environmental Health
The ANA’s Environmental Health standard states, “The registered nurse practices in a manner that advances environmental safety and health.”[47]
Read about promoting workplace safety for nurses in the “Safety” chapter in Open RN Nursing Fundamentals, 2e.[48]
Read about fostering a professional environment that does not tolerate abusive behaviors in the “Collaboration Within the Interprofessional Team” chapter of this book.
Read about addressing the impacts of social determinants of health in the “Advocacy” chapter of this book.
Learning Objectives
- Prioritize nursing care based on patient acuity
- Use principles of time management to organize work
- Analyze effectiveness of time management strategies
- Use critical thinking to prioritize nursing care for patients
- Apply a framework for prioritization (e.g., Maslow, ABCs)
“So much to do, so little time.” This is a common mantra of today’s practicing nurse in various health care settings. Whether practicing in acute inpatient care, long-term care, clinics, home care, or other agencies, nurses may feel there is "not enough of them to go around.”
The health care system faces a significant challenge in balancing the ever-expanding task of meeting patient care needs with scarce nursing resources that has even worsened as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. Many health care organizations have seen exacerbation in nurse turnover post-pandemic as nurses struggle with increasing stress, burnout, and feeling of uncertainty within the profession.[49] A recent nursing survey done by the American Nurses Foundation found that 60% of nurses reported extremely stressful, violent, and traumatic events as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.[50] Additionally, a staggering 89% of nurses reported that their organizations experience significant staffing shortages.[51]
With a limited supply of registered nurses, nurse managers are often challenged to implement creative staffing practices such as sending staff to units where they do not normally work (i.e., floating), implementing mandatory staffing and/or overtime, utilizing travel nurses, or using other practices to meet patient care demands.[52] Staffing strategies can result in nurses experiencing increased patient assignments and workloads, extended shifts, or temporary suspension of paid time off. Nurses may receive a barrage of calls and text messages offering “extra shifts” and bonus pay, and although the extra pay may be welcomed, they often eventually feel burnt out trying to meet the ever-expanding demands of the patient-care environment.
A novice nurse who is still learning how to navigate the complex health care environment and provide optimal patient care may feel overwhelmed by these conditions. Novice nurses frequently report increased levels of stress and disillusionment as they transition to the reality of the nursing role.[53] How can we address this professional dilemma and enhance the novice nurse's successful role transition to practice? The novice nurse must enter the profession with purposeful tools and strategies to help prioritize tasks and manage time so they can confidently address patient care needs, balance role demands, and manage day-to-day nursing activities.
Let’s take a closer look at the foundational concepts related to prioritization and time management in the nursing profession.

